Beginning Of The New Age
Dr. Rajnikant Parmar M.CH IN PLASTIC SURGERY
Experience the best in medical and cosmetic care at Krisha Hospital, led by Dr. Rajnikant Parmar, M.CH in Plastic Surgery. Our hospital is dedicated to providing advanced treatments with a highly qualified team of doctors, nurses, and support staff who ensure each patient receives personalized and compassionate care.
Dr. Rajnikant Parmar is recognized as the only plastic surgeon in Vadodara performing hair transplants independently, with over 2,500 successful procedures completed. At Krisha Hospital, patients benefit from world-class expertise, state-of-the-art technology, and a commitment to safety and satisfaction for every treatment. Book your consultation to discover how you can achieve your desired results with confidence.
Who We Are
Dr. Rajnikant Parmar is a Gold Medalist in M.CH Plastic Surgery from M.S. University, Vadodara—one of the most respected institutes for Plastic, Reconstructive, and Cosmetic Surgery. With extensive knowledge and experience in a wide range of cosmetic and plastic surgery procedures, Dr. Parmar has been practicing in Vadodara for the past five years.
He has also trained alongside world-renowned aesthetic surgeons, including Dr. Kotaro from Japan. This international exposure and dedication to excellence enable Dr. Parmar to deliver advanced, safe, and effective treatments for every patient at Krisha Hospital.




Seeking the Premier Cosmetic Surgeon in Vadodara?
HAIR TRANSPLANT
Get effective hair transplant solutions at Krisha Hospital with proven results and affordable pricing.

OBESITY SURGERY
Achieve lasting weight loss with advanced obesity surgery—an effective option beyond diet and exercise.

COSMETIC SURGERY
Enhance your appearance with cosmetic procedures for hair, face, chest, and more.
BREAST SURGERY
Improve breast shape and confidence with specialized breast surgery for women.

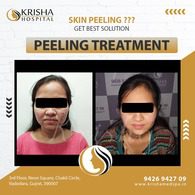
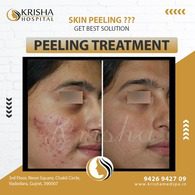
SKIN TREATMENTS
Experience safe, painless, and lasting skin treatments at Krisha Hospital in Vadodara.

COSMETIC DENTISTRY
Maintain healthy teeth and gums with comprehensive cosmetic dental care.
Our Complete List Of Procedures
Hair
OBESITY
COSMETICS
Our Popular Procedures

Acne Treatment
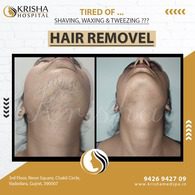
Laser Hair Removal Treatment

Dark Circle Removal Treatment

Non Surgical Face Lift Treatment

Anti Ageing, Wrinkle Treatment

Chemical Peels Treatment
Laser Tattoo Removal
Things To Know
Each year, millions of people worldwide undergo cosmetic surgery, with the United States alone reporting hundreds of thousands of procedures annually. The global number fluctuates based on trends, technology, and accessibility, but cosmetic enhancements remain highly popular across many regions.
Cosmetic surgery can be performed under either general or local anesthesia, depending on the procedure’s complexity. General anesthesia is used for extensive surgeries, while local anesthesia numbs a specific area, allowing the patient to remain awake but comfortable.
Plastic surgery with general anesthesia can be safe for patients with heart conditions when managed by experienced professionals. Comprehensive pre-operative assessment and careful monitoring during and after surgery help minimize risks, making the procedure possible for many with controlled heart issues.
Recovery varies by procedure and individual healing. Most patients experience swelling and discomfort initially, with improvement over weeks. Following post-op instructions and attending follow-ups helps ensure a smooth recovery. Normal activities can often resume within days to weeks, but full results may take several months.
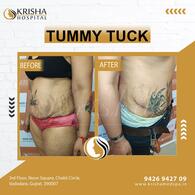
Plastic surgery can be performed on the face, breasts, abdomen, extremities, and skin. Common procedures include facelifts, rhinoplasty, breast augmentation, tummy tucks, liposuction, and reconstructive surgeries. Treatments are tailored to enhance aesthetics or correct deformities for natural-looking results.
The duration of cosmetic surgery depends on the procedure. Minor treatments like fillers may take minutes, while surgeries such as breast augmentation or facelifts can last several hours. Your surgeon will provide an estimated time based on your chosen procedure.
Risks of cosmetic surgery include infection, bleeding, scarring, nerve damage, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Other possible complications are asymmetry, dissatisfaction with results, or slow healing. Choosing a qualified surgeon and following post-operative care instructions significantly reduces these risks.
The most common cosmetic surgeries are breast augmentation, liposuction, rhinoplasty (nose reshaping), eyelid surgery (blepharoplasty), and abdominoplasty (tummy tuck). Non-surgical treatments like Botox and dermal fillers are also very popular.
Cosmetic surgery is usually not covered by medical insurance unless it is medically necessary, such as for injury repair or correcting birth defects. Purely elective, aesthetic procedures are typically excluded from coverage.
Cosmetic surgery is elective and focuses on enhancing appearance for aesthetic reasons, such as facelifts or breast augmentation. Reconstructive surgery aims to restore function and normal appearance after trauma, congenital defects, or medical conditions, like breast reconstruction after mastectomy or repairing cleft lips.
Recovery time depends on the procedure’s complexity and the patient’s health. Initial healing often takes weeks to months, with gradual return to normal activities as advised by your surgeon.
Reconstructive surgery includes breast reconstruction, cleft lip and palate repair, scar revision, hand surgery, burn repair, and facial reconstruction after trauma or cancer. These procedures restore function and appearance
All surgical procedures, including plastic and cosmetic surgery, will result in some scarring. Skilled surgeons use advanced techniques and place incisions in less visible areas to minimize scars. With proper post-operative care—like silicone sheets, scar massage, sun protection, and sometimes laser therapy—scars can often be made less noticeable over time. However, it is not possible to have surgery without any scars at all.
Plastic surgery includes specialized fields such as hand surgery, craniofacial surgery for facial and skull deformities, microsurgery for repairing small nerves and tissues, and aesthetic surgery for appearance enhancement. Each area requires specific expertise to address both function and aesthetics for optimal patient results.

About Us
Our Statistics
8456 +
Happy Client
5673 +
Surgery Performed
15 +
Year Of Experience
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Krisha hospital ma me brest size mate consulting karyu d .r rajnikant sir jode Mane ghanu saru samjavyu chhe thanks sirPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Me krisha hospital ma hair fall ni treatment lidhi chhe mane ghanu saru result madiyu chhe thanks for krisha hospitalPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very nice Krisha Hoshpital na all's Sister and Doctor Rajanikant parmar aap shau a mane bahuj sharsh halp Sarwish aapi mane Pahela karta atiyare bahuj sharu fil thay che Thank u so much doctor &shatap Shalam che tamne Doctor Rajanikant shahenPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Really happy with service. One of the best clinicPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Amazing worked on my face by rajnikant sir.. I have many stitches on my face but after recovery no marks on my face.. Thank you very much..Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Krisha hospital me mene skin glow ke liye haydra facial karvaya tha nice result Thanks sir & staffPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. All cosmatic surgerys are excellent specially Hair Transplant & Tummy TuckPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Mene Hair Transplant Surgery Karvai he or mujhe bohot excellent result Mila he or me or bhi loggo prefere karunga So thank uuu krisha hospitalPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best Hair Transplant & Hair Loss Surgery In Vadodara City
Our Esteemed Client